In this blog, we will understand what is cryptocurrency mining and how does it work?
Before we start, please subscribe to our newsletter so you never miss an article from us.
Please read the article on “What is a cryptocurrency and how it works” to better understand “What is Cryptocurrency Mining and How does it work”.
It is important to understand that cryptocurrency mining has evolved a lot in the last 5 years just like the blockchain evolved in the last 5 years but the base concept of these remains the same.
Who are these miners?
Cryptocurrencies are issued by a blockchain network according to a set of predetermined algorithms.
Miners typically need large rigs of reliable, application-specific hardware to have a decent chance at being the first to verify and secure the block.

They use hardware to run algorithms on specific software to verify transactions on the blockchain which then gets added to the public ledger.
Miners power up the network by solving the mathematical problems that confirm transactions
In exchange, miners receive newly-created coins as a reward for their work.
What is a cryptocurrency mining ?
It’s one of the key elements that allow cryptocurrencies to work as a peer-to-peer decentralized network without the need for a third-party central authority.
It is a process in which transactions between users are verified and added into the blockchain public ledger, and also a process that is used to introduce new coins into the existing circulating supply.
How does it work?
A miner is a node in the network that collects transactions and works to organize them into blocks whenever transactions are made.
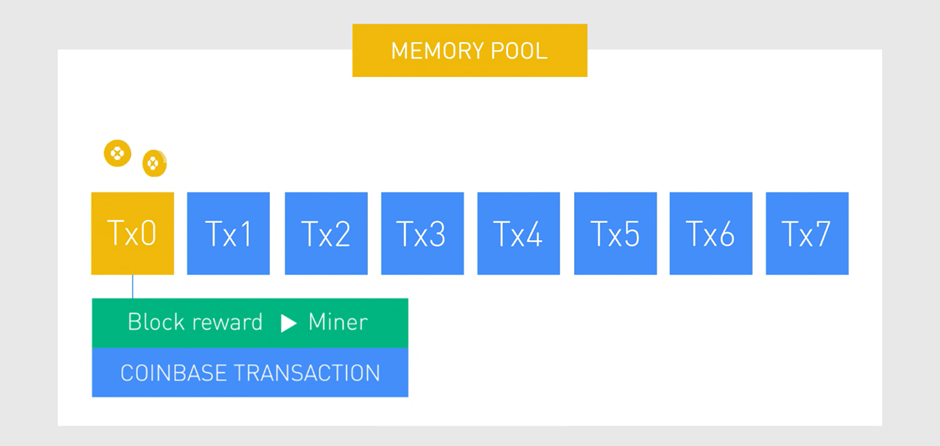
Miner nodes receive and verify the transactions add them into the memory pool and begin assembling them into a block of multiple transactions.

The first step in a process of mining a block is to hash each transaction in the memory pool before starting the process.
The miner node adds the transaction where they send themselves to mining reward.
This transaction is referred to as the Coinbase transaction. It’s a transaction where coins get created out of thin air and in most cases, is the first transaction in a new block.
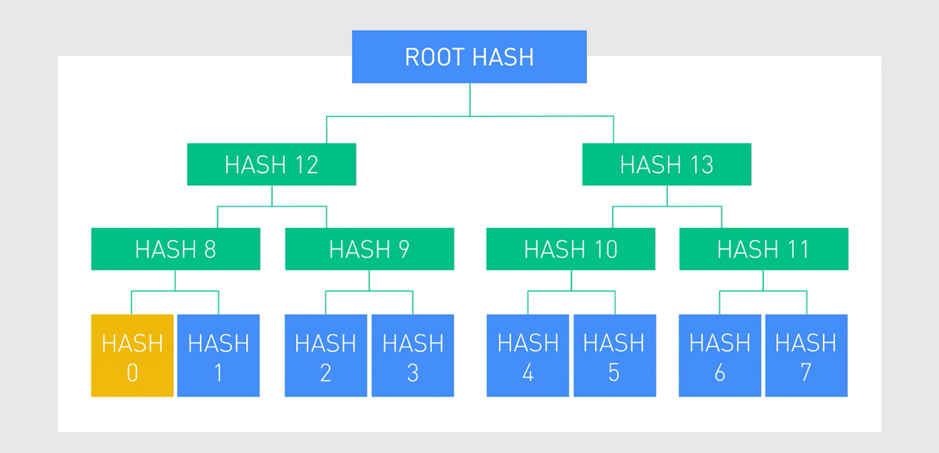
After every transaction is hashed, these hashes are then organized into something called a hash tree, meaning that the hashes are organized into pairs and then hashed again until the top of the tree is reached.
Root Hash
It is also known as a root hash or a Merkle root, the root hash along with the hash from the previous block and the random number called NONCE, is then placed into the block’s header.
The blocks header is then hashed, producing an output that will serve as the Blocks identifier.
The blocks identifier must be less than a certain target value that is set by the protocol. In other words, the block header hash must start with a certain number of zeros.

This target value, also known as the hashing difficulty, scales, ensuring that the rate at which new blocks are created remains proportionate to the amount of hashing power in the network.
The miners keep hashing the header over and over again by iterating through the nonce until one miner in the network eventually produces a valid hash.
Hashing in Cryptography
When a valid hash is found, the founder node will broadcast the block to the network.
All the other nodes will check if the hashes are valid add the block into their copy of the blockchain and move on to mining the next block.

However, sometimes it happens that two miners broadcast a valid block at the same time and the network ends up with two competing blocks.
How Miners Handle transactions ?
Miners start to mine the next block based on the block they received first.
The competition between these blocks will continue until the next block is mined, based on either one of the competing blocks.
The block that gets abandoned is called an orphan block or a stale block.

The miners of this block will switch back to mining the chain of the winner block, while the block reward is granted to the miner who discovers the valid hash first.
Problem Faced by Miners
The probability of finding the hash is equal to the proportion of the total mining power on the network.
Miners with a small percentage of the mining power stand a very small chance of discovering the next block on their own.
As the invention of cryptocurrency has given rise to several domains, cryptocurrency mining has multi-folded in these years.
Mining costs a lot of electricity to the miners where the miners solve complex mathematical problems to add a particular block to the blockchain.
As the number of miners increases, trying to crack the code, the difficulty of the complex algorithm increases.
Several miners have joined together to create a mining pool that helps the miners as the total number of miners doesn’t increase concerning the blockchain.
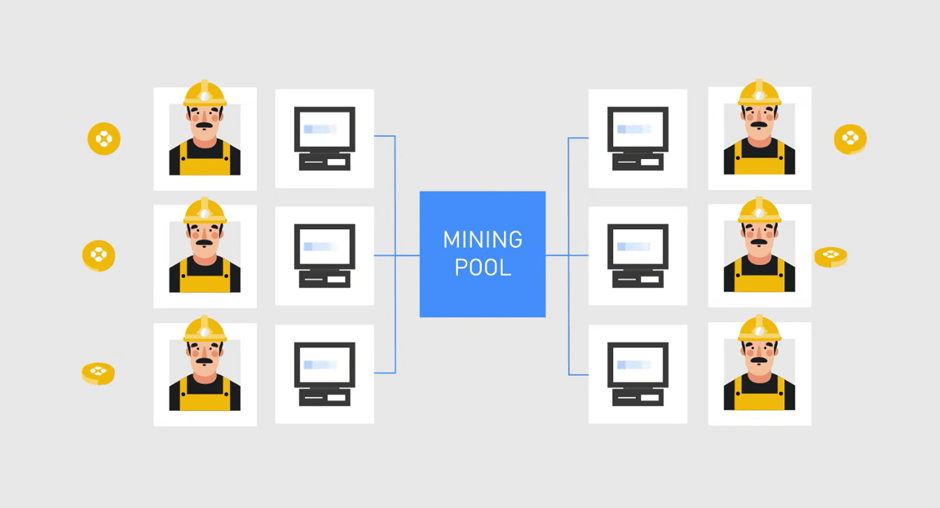
A whole set of miners act as a single miner . Hence the difficulty of the complex algorithms is not increased as the number of miners is increased in the mining pool.
It means the pooling of resources by miners who share their processing power over a network equally among everyone in the pool according to the amount of work they contribute to the probability of finding a block.
In other words, in a mining pool the set of miners share the work among themselves . Block Reward is also shared among them in proportions of their work .
So this is how Cryptocurrency Miners and Cryptocurrency mining works.
Hope you liked our article on “What is Cryptocurrency mining” . Please read our other articles on articles “Next Cryptocurrency to Explode 2022”

